Hydrogen fuel cells in SUVs convert hydrogen gas into electricity to power the vehicle, producing only water and heat as byproducts. This innovative technology offers a clean, efficient alternative to gasoline, combining long driving ranges with fast refueling times—perfect for eco-conscious drivers who need space and power.
Imagine driving a spacious, powerful SUV that doesn’t pollute the air—no tailpipe emissions, no oil changes, and no long waits at charging stations. Sounds too good to be true? It’s not. Thanks to hydrogen fuel cell technology, this future is already here. Hydrogen fuel cell SUVs are quietly revolutionizing the way we think about clean transportation, blending the practicality of traditional SUVs with the environmental benefits of zero-emission driving.
Unlike battery-electric vehicles that rely on heavy lithium-ion batteries, hydrogen-powered SUVs generate electricity on board using a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen. This process powers an electric motor, just like in a battery EV, but without the need for lengthy charging. The result? A vehicle that’s clean, efficient, and capable of long-distance travel—perfect for families, road trips, and daily commutes alike.
As climate change concerns grow and governments push for greener transportation, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) are gaining traction as a viable alternative to gasoline and diesel. While still a niche market compared to electric vehicles, hydrogen SUVs offer unique advantages that make them especially appealing for larger vehicles. They’re quiet, powerful, and refuel in minutes—not hours. And because they produce only water as a byproduct, they’re a true zero-emission solution when powered by green hydrogen.
Key Takeaways
- Zero Emissions: Hydrogen fuel cell SUVs emit only water vapor, making them one of the cleanest vehicles on the road.
- Long Driving Range: Most hydrogen SUVs can travel 300–400 miles on a single tank, rivaling traditional gasoline vehicles.
- Fast Refueling: Refilling a hydrogen tank takes just 3–5 minutes, much faster than charging an electric vehicle.
- Quiet and Smooth Performance: Fuel cells operate silently and deliver instant torque for a smooth, responsive drive.
- Ideal for Large Vehicles: SUVs benefit from the compact size and high energy density of hydrogen fuel cells, preserving cabin and cargo space.
- Emerging Infrastructure: While hydrogen stations are still limited, growth is accelerating, especially in California and parts of Europe.
- Sustainable with Green Hydrogen: When hydrogen is produced using renewable energy, the entire lifecycle becomes carbon-neutral.
📑 Table of Contents
What Are Hydrogen Fuel Cells and How Do They Work?
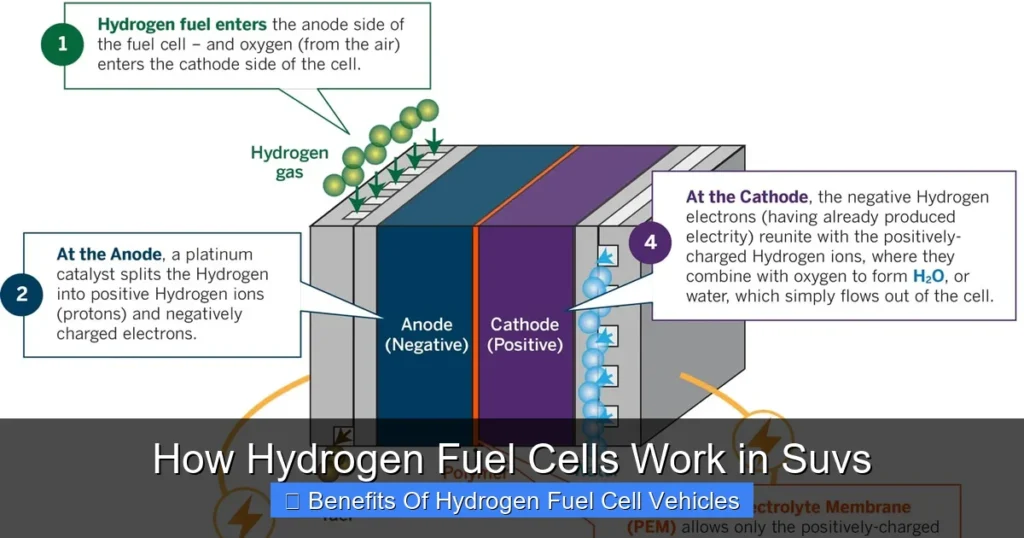
At the heart of every hydrogen fuel cell SUV is a device called a proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cell. This compact, high-tech unit is responsible for converting hydrogen gas into electricity—cleanly and efficiently. But how exactly does it work? Let’s break it down in simple terms.
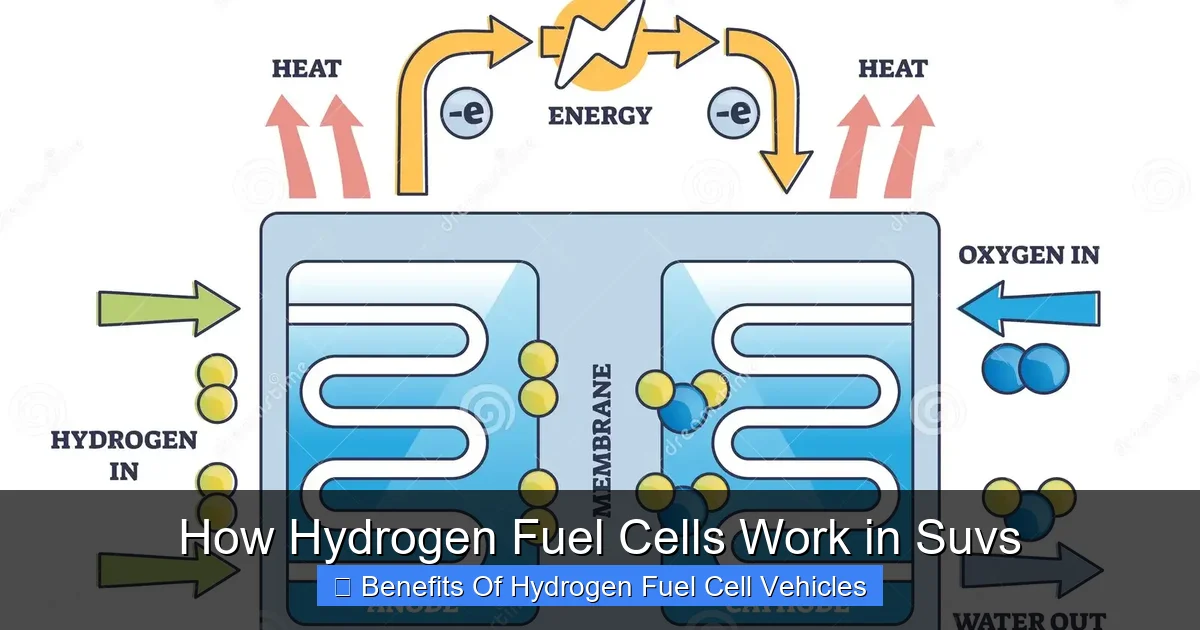
Inside the fuel cell, hydrogen gas (H₂) from the onboard tank is fed into the anode side of the cell. At the anode, a catalyst—usually platinum—splits the hydrogen molecules into protons and electrons. The protons pass through a special membrane (the proton exchange membrane) to the cathode side, while the electrons are forced to travel through an external circuit. This flow of electrons is what we call electricity. That electricity then powers the SUV’s electric motor, just like in a battery-electric vehicle.
Meanwhile, on the cathode side, oxygen from the air combines with the protons and electrons to form water (H₂O)—the only emission. Heat is also produced as a byproduct, which is managed by the vehicle’s cooling system. The entire process is silent, efficient, and produces zero harmful emissions.
The Role of the Fuel Cell Stack
A single fuel cell produces only about 0.6 to 0.8 volts—far too little to power a vehicle. That’s why multiple fuel cells are stacked together to form a “fuel cell stack.” A typical hydrogen SUV might use a stack containing hundreds of individual cells. When combined, they generate enough electricity—usually between 80 and 120 kilowatts—to power the vehicle’s motor and auxiliary systems.
The stack is designed to be compact and lightweight, which is crucial for SUVs where space and weight are key considerations. Modern fuel cell stacks are also highly durable, with lifespans exceeding 100,000 miles under normal driving conditions. Advances in materials and manufacturing are continually improving efficiency and reducing costs, making fuel cells more accessible.
Hydrogen Storage: Safe and Efficient
One of the biggest challenges with hydrogen is storing it safely and efficiently. Unlike gasoline, hydrogen is a gas at room temperature and must be compressed to extremely high pressures—typically 5,000 to 10,000 psi—to fit enough energy into a reasonable tank size. That’s why hydrogen SUVs use high-strength carbon fiber tanks that can withstand these pressures without leaking or rupturing.
These tanks are rigorously tested and designed to meet strict safety standards. In the event of a crash, they’re built to vent hydrogen safely away from the vehicle, minimizing fire risk. In fact, hydrogen is lighter than air and disperses quickly, reducing the chance of ignition compared to gasoline vapors.
Most hydrogen SUVs carry between 4 and 6 kilograms of hydrogen, which provides a driving range of 300 to 400 miles—comparable to many gasoline-powered SUVs. Refueling is simple: you pull up to a hydrogen station, connect the nozzle, and fill up in just 3 to 5 minutes. No waiting, no range anxiety.
Why Hydrogen Fuel Cells Are Ideal for SUVs
Visual guide about How Hydrogen Fuel Cells Work in Suvs
Image source: thumbs.dreamstime.com
SUVs are known for their size, power, and versatility—but they’re also traditionally associated with high fuel consumption and emissions. Hydrogen fuel cells offer a way to keep the benefits of SUVs while eliminating their environmental drawbacks. Here’s why this technology is a natural fit.
High Energy Density and Long Range
One of the biggest advantages of hydrogen is its high energy density by weight. Hydrogen contains about three times more energy per pound than gasoline. This means that even though hydrogen tanks take up space, they can store a lot of energy without adding excessive weight. For large vehicles like SUVs, which need to carry passengers, cargo, and powerful drivetrains, this is a major benefit.
Battery-electric SUVs, by contrast, require large, heavy battery packs to achieve similar ranges. For example, a Tesla Model X has a battery pack weighing over 1,200 pounds. A hydrogen-powered SUV like the Toyota Mirai or Hyundai NEXO uses a much lighter fuel cell system and hydrogen tanks, freeing up space and reducing overall vehicle weight.
This efficiency translates into longer driving ranges. The Hyundai NEXO, for instance, offers an EPA-estimated range of 380 miles—more than many gasoline SUVs. That makes it ideal for long road trips, rural driving, or areas with limited charging infrastructure.
Fast Refueling for Busy Lifestyles
Let’s face it: no one likes waiting. Charging an electric SUV can take anywhere from 30 minutes (with fast charging) to several hours (with home charging). For families on the go, frequent stops and long charging times can be a major inconvenience.
Hydrogen fuel cell SUVs solve this problem with near-instant refueling. At a hydrogen station, the process is similar to filling up a gas tank—just pull up, connect the nozzle, and wait 3 to 5 minutes. No need to plan your trip around charging stations or worry about battery degradation from frequent fast charging.
This makes hydrogen SUVs especially appealing for people who value convenience and time. Whether you’re commuting daily, taking weekend trips, or using your SUV for work, the ability to refuel quickly is a game-changer.
Preserving Interior and Cargo Space
Another advantage of hydrogen fuel cells is their compact design. Unlike battery packs, which can take up significant space under the floor or in the trunk, fuel cell systems are relatively small and can be integrated into the vehicle’s frame without sacrificing passenger or cargo room.
For example, the Toyota Mirai has a sleek, spacious interior with plenty of legroom and a large trunk—something that’s harder to achieve in battery-electric SUVs with bulky batteries. This makes hydrogen SUVs a great choice for families, outdoor enthusiasts, or anyone who needs a roomy, practical vehicle.
Quiet and Smooth Driving Experience
Hydrogen fuel cell SUVs are electric vehicles at their core, which means they deliver the same quiet, smooth performance as battery EVs. There’s no engine noise, no gear shifts, and instant torque from a standstill. The result is a refined, comfortable ride that’s perfect for city driving and highway cruising.
The fuel cell system itself operates silently, with no moving parts other than the compressor and cooling fans. This contributes to a peaceful cabin environment, making long drives more enjoyable.
Real-World Examples of Hydrogen Fuel Cell SUVs
While still a small segment of the auto market, several automakers have launched hydrogen fuel cell SUVs that showcase the technology’s potential. These vehicles offer a glimpse into what the future of clean, powerful transportation could look like.
Hyundai NEXO
The Hyundai NEXO is one of the most advanced hydrogen SUVs on the market. It features a 95-kilowatt fuel cell stack and a 4.2-kilogram hydrogen tank, delivering an EPA-estimated range of 380 miles. The NEXO also includes advanced driver assistance systems, a premium interior, and a sleek, aerodynamic design.
One standout feature is its air purification system, which filters out 99.9% of fine dust and pollutants from the air as it drives—effectively cleaning the environment while you drive. It’s a bold statement about the role hydrogen vehicles can play in improving air quality.
Toyota Mirai
Toyota has been a pioneer in hydrogen technology, and the Mirai is its flagship fuel cell vehicle. The latest generation offers a more spacious interior, improved performance, and a range of up to 402 miles. With its rear-wheel-drive platform and low center of gravity, the Mirai delivers a sporty, engaging driving experience.
Toyota also offers the Mirai with a “Green Package” that includes sustainable materials like bio-fabric seats and recycled plastics. It’s a holistic approach to sustainability that goes beyond just zero emissions.
BMW iX5 Hydrogen
BMW has entered the hydrogen SUV market with the iX5 Hydrogen, a concept vehicle based on the popular X5 platform. It combines BMW’s luxury and performance with hydrogen fuel cell technology, offering a glimpse into what premium hydrogen SUVs could look like.
The iX5 Hydrogen features a fuel cell system developed in partnership with Toyota and can be refueled in under four minutes. While not yet widely available, it signals BMW’s commitment to exploring alternative powertrains.
Mercedes-Benz GLC F-CELL
Mercedes-Benz has also experimented with hydrogen, offering the GLC F-CELL—a plug-in hybrid that combines a hydrogen fuel cell with a small battery. This dual-system approach allows for short electric-only trips using the battery, while the fuel cell provides extended range for longer drives.
Though production has been limited, the GLC F-CELL demonstrates how hydrogen can be integrated into existing vehicle platforms with minimal disruption.
Challenges and Limitations of Hydrogen SUVs
Despite their many benefits, hydrogen fuel cell SUVs face several challenges that have slowed widespread adoption. Understanding these limitations is key to appreciating the technology’s current state and future potential.
Limited Hydrogen Refueling Infrastructure
The biggest hurdle for hydrogen vehicles is the lack of refueling stations. As of 2024, there are fewer than 100 public hydrogen stations in the United States, with most located in California. This makes it difficult for drivers outside these areas to own and operate a hydrogen SUV.
While countries like Japan, South Korea, and Germany are investing heavily in hydrogen infrastructure, the U.S. lags behind. Without a reliable network of stations, range anxiety remains a real concern—even if the vehicle itself can travel hundreds of miles.
High Production and Distribution Costs
Hydrogen is expensive to produce, transport, and store. Most hydrogen today is made from natural gas through a process called steam methane reforming, which emits carbon dioxide. This “gray hydrogen” undermines the environmental benefits of fuel cell vehicles.
“Green hydrogen,” produced using renewable energy and electrolysis, is cleaner but much more expensive. Scaling up green hydrogen production will require significant investment in renewable energy and electrolyzer technology.
Competition from Battery Electric Vehicles
Battery-electric SUVs like the Tesla Model Y, Ford Mustang Mach-E, and Rivian R1S have gained massive popularity due to falling battery prices, expanding charging networks, and strong consumer interest. These vehicles offer many of the same benefits as hydrogen SUVs—zero emissions, quiet operation, and low running costs—but with more established infrastructure.
For many consumers, the convenience of home charging and the growing availability of fast chargers make battery EVs a more practical choice—at least for now.
Vehicle Cost and Availability
Hydrogen SUVs are still expensive, with prices often exceeding $60,000. The Hyundai NEXO, for example, starts around $60,000, and the Toyota Mirai is similarly priced. In contrast, many battery-electric SUVs are now available under $50,000, with federal and state incentives further reducing the cost.
Additionally, hydrogen SUVs are only available in select markets, limiting consumer access. Most are sold in California, where hydrogen stations are concentrated.
The Future of Hydrogen Fuel Cell SUVs
Despite the challenges, the future of hydrogen fuel cell SUVs looks promising. Governments, automakers, and energy companies are investing billions in hydrogen technology, recognizing its potential to decarbonize transportation, especially for heavy-duty and long-range vehicles.
Growing Investment in Green Hydrogen
Countries around the world are launching national hydrogen strategies to promote clean hydrogen production. The European Union, for example, aims to install 40 gigawatts of electrolyzer capacity by 2030. The U.S. Department of Energy has launched the “Hydrogen Shot” initiative, aiming to reduce the cost of clean hydrogen to $1 per kilogram within a decade.
As green hydrogen becomes cheaper and more widely available, the environmental case for hydrogen SUVs will only strengthen.
Expansion of Refueling Networks
Automakers and energy companies are partnering to build more hydrogen stations. Toyota, Shell, and Air Liquide are among the companies investing in hydrogen infrastructure in California and beyond. Mobile refueling units and truck-based hydrogen delivery are also being tested to serve remote areas.
In Europe, countries like Germany and France are building hydrogen corridors along major highways, enabling long-distance travel.
Technological Advancements
Research is ongoing to improve fuel cell efficiency, reduce the use of expensive materials like platinum, and extend the lifespan of fuel cells. Solid-state hydrogen storage and liquid organic hydrogen carriers (LOHCs) are emerging as potential alternatives to high-pressure tanks, offering safer and more efficient storage.
These innovations could make hydrogen SUVs lighter, cheaper, and more practical in the coming years.
Policy Support and Incentives
Governments are offering incentives to encourage hydrogen vehicle adoption. In the U.S., the Inflation Reduction Act includes tax credits for hydrogen production and fuel cell vehicles. California offers rebates of up to $15,000 for hydrogen vehicle purchases and free hydrogen refueling for the first few years.
As policies evolve and infrastructure grows, hydrogen SUVs could become a mainstream option for eco-conscious drivers.
Is a Hydrogen Fuel Cell SUV Right for You?
So, should you consider a hydrogen fuel cell SUV? The answer depends on your driving habits, location, and environmental priorities.
If you live in an area with hydrogen stations—like California—and value long range, fast refueling, and zero emissions, a hydrogen SUV could be an excellent choice. It’s ideal for families, commuters, and anyone who wants the space and power of an SUV without the environmental guilt.
However, if you’re outside the current hydrogen network or prefer the convenience of home charging, a battery-electric SUV might be more practical—for now.
Ultimately, hydrogen fuel cell SUVs represent a bold step toward a cleaner, more sustainable future. While challenges remain, the technology is evolving rapidly, and the benefits are hard to ignore. As infrastructure expands and costs come down, hydrogen could play a key role in the transition to zero-emission transportation.
Conclusion
Hydrogen fuel cells offer a compelling solution for powering SUVs—combining the space, performance, and convenience drivers love with the environmental benefits of zero emissions. By converting hydrogen into electricity on board, these vehicles produce only water and heat, making them one of the cleanest options on the road.
With long driving ranges, fast refueling, and quiet operation, hydrogen SUVs are well-suited for modern lifestyles. Real-world models like the Hyundai NEXO and Toyota Mirai demonstrate the technology’s potential, while ongoing advancements in green hydrogen and infrastructure promise a brighter future.
While challenges like limited stations and high costs remain, the momentum behind hydrogen is growing. For drivers who want a powerful, practical, and planet-friendly SUV, hydrogen fuel cells are worth watching—and possibly driving—in the years ahead.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do hydrogen fuel cells work in SUVs?
Hydrogen fuel cells in SUVs generate electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen. The electricity powers an electric motor, producing only water and heat as byproducts—no harmful emissions.
Are hydrogen fuel cell SUVs really zero emission?
Yes, hydrogen fuel cell SUVs emit only water vapor from the tailpipe. However, the overall environmental impact depends on how the hydrogen is produced—green hydrogen from renewable sources is truly zero emission.
How long does it take to refuel a hydrogen SUV?
Refueling a hydrogen SUV takes just 3 to 5 minutes, similar to filling up a gasoline vehicle. This is much faster than charging a battery-electric SUV, which can take 30 minutes to several hours.
What is the driving range of a hydrogen fuel cell SUV?
Most hydrogen SUVs offer a range of 300 to 400 miles on a full tank, comparable to many gasoline-powered SUVs. For example, the Hyundai NEXO has an EPA-estimated range of 380 miles.
Where can I refuel a hydrogen SUV?
Hydrogen refueling stations are currently limited, with most located in California. A few stations exist in other states and countries like Japan, Germany, and South Korea, but infrastructure is still developing.
Are hydrogen SUVs safe?
Yes, hydrogen SUVs are designed with safety in mind. High-strength carbon fiber tanks store hydrogen safely, and the gas disperses quickly in the event of a leak, reducing fire risk compared to gasoline.